Introduction
In today’s digital age, data centers are the nerve centers of organizations, housing critical data and applications that drive business operations. With the increasing reliance on cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT), the volume of sensitive information stored in data centers is growing exponentially. This makes data centers prime targets for cyberattacks, physical breaches, and other security threats. Protecting sensitive information in data centers is paramount for any organization, and implementing best practices for data center security is essential for safeguarding critical assets.
Definition
The entire suite of physical, network, and procedural safeguards that are put in place to keep unauthorized access, cyberattacks, and other possible dangers away from a data center’s hardware, software, and data is known as data center security. It involves safeguarding sensitive information through practices such as access control, encryption, network segmentation, and continuous monitoring, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data stored and processed in the facility. Effective data center security is essential for maintaining operational resilience and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Understanding Data Center Security
Data center security encompasses the physical and virtual security measures designed to protect the infrastructure, hardware, software, and data within a data center. This includes securing access to the data center, monitoring and managing network traffic, safeguarding against cyber threats, and ensuring data privacy and integrity. A comprehensive approach to data center security involves multiple layers of protection to address both internal and external threats.
Physical Security Measures
Perimeter Security:
The first line of defense in data center security is the physical perimeter. Implementing robust perimeter security measures is crucial to prevent unauthorized access to the facility. This includes fencing, security guards, surveillance cameras, and access control systems. Advanced technologies such as biometric scanners and facial recognition can further enhance perimeter security by ensuring that only authorized personnel can enter the data center.
Controlled Access:
Access to sensitive areas within the data center should be restricted to authorized personnel only. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) can help ensure that only individuals with the necessary permissions can access critical systems and data. Physical access logs should be maintained to track who enters and exits the facility, providing an audit trail for security purposes.
Environmental Controls:
Environmental elements that might affect data centre operations’ security and integrity include humidity, temperature, and power supply. Implementing environmental controls, such as fire suppression systems, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and climate control systems, can help mitigate the risk of environmental hazards. Regular maintenance and monitoring of these systems are essential to ensure they function correctly in the event of an emergency.
Network Security Measures
Firewall Protection:
Firewalls are a critical component of data center network security.They filter inbound and outgoing traffic in accordance with pre-established security criteria, serving as a barrier between the internal network and external threats. Implementing next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) with advanced threat detection capabilities can provide enhanced protection against sophisticated cyberattacks, such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks and malware infiltration.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS):
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) play a crucial role in monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity and preventing unauthorized access to the data center. These systems use advanced algorithms to detect and respond to potential threats in real time, helping to minimize the impact of cyberattacks. IDPS solutions should be regularly updated to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Network Segmentation:
Network segmentation involves dividing the data center network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the spread of cyber threats. By segmenting the network, organizations can restrict access to sensitive information and contain potential breaches within a specific segment, minimizing the risk of data exposure. Virtual LANs (VLANs) and software-defined networking (SDN) can be used to provide network segmentation, which can increase overall data centre resilience and network security.
Data Security Measures
Data Encryption:
One of the best methods for preventing illegal access to sensitive data is data encryption. By encrypting data both at rest and in transit, organizations can ensure that even if data is intercepted or stolen, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties. Implementing strong encryption protocols, such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and Transport Layer Security (TLS), is essential for safeguarding sensitive data in the data center.
Data Masking and Tokenization:
Data masking and tokenization are techniques used to obfuscate sensitive information, making it difficult for unauthorized users to access or interpret the data. Whereas sensitive data is replaced with fake data in data masking, tokenisation substitutes sensitive data with a token that can only be traced back to the real data by authorised systems. These techniques are particularly useful for protecting personally identifiable information (PII) and payment card data in compliance with regulatory requirements.
Data Backup and Recovery:
Data backup and recovery are critical components of data center security. Regularly backing up data ensures that organizations can quickly recover from data loss incidents, such as hardware failures, cyberattacks, or natural disasters. Implementing a comprehensive data backup strategy that includes off-site and cloud backups can provide additional protection against data loss. Additionally, organizations should regularly test their data recovery processes to ensure that they can restore data quickly and efficiently in the event of an emergency.
Cybersecurity Measures
Threat Intelligence and Monitoring:
Threat intelligence involves gathering and analyzing information about potential cyber threats to the data center. By leveraging threat intelligence, organizations can proactively identify and mitigate security risks before they escalate into significant incidents. Implementing continuous monitoring solutions, such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, can help detect and respond to security events in real-time, improving the overall security posture of the data center.
Patch Management:
Keeping software and systems up to date with the latest security patches is essential for protecting the data center from known vulnerabilities. Organizations should implement a robust patch management process that includes regular vulnerability assessments, patch testing, and deployment. Automated patch management solutions can help streamline this process, ensuring that all systems are promptly updated to mitigate security risks.
Incident Response Planning:
Despite the best security measures, no data center is entirely immune to security incidents. Having a well-defined incident response plan is crucial for minimizing the impact of security breaches and ensuring a swift recovery. The incident response plan should outline the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident, including identifying and containing the breach, assessing the damage, and communicating with stakeholders. Regular drills and simulations can help ensure that the incident response team is prepared to handle real-world scenarios effectively.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Data Protection Regulations:
Compliance with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), is a critical aspect of data center security. These regulations impose strict requirements on how organizations handle, store, and protect sensitive information. Implementing robust data protection measures, such as encryption, access controls, and data anonymization, can help organizations meet regulatory requirements and avoid costly fines and penalties.
Security Audits and Assessments:
Regular security audits and assessments are essential for evaluating the effectiveness of data center security measures and identifying potential vulnerabilities. Organizations should conduct both internal and external audits to assess compliance with security policies, standards, and regulations. Third-party assessments can provide an unbiased evaluation of the data center’s security posture and offer recommendations for improvement.
Employee Training and Awareness:
In data centers, one of the main reasons for data breaches is human mistakes. To lower the danger of unintentional data disclosure, training staff members on data center security best practices is essential. Regular training sessions, security awareness programs, and phishing simulations can help employees recognize and respond to potential security threats, improving the overall security culture within the organization.
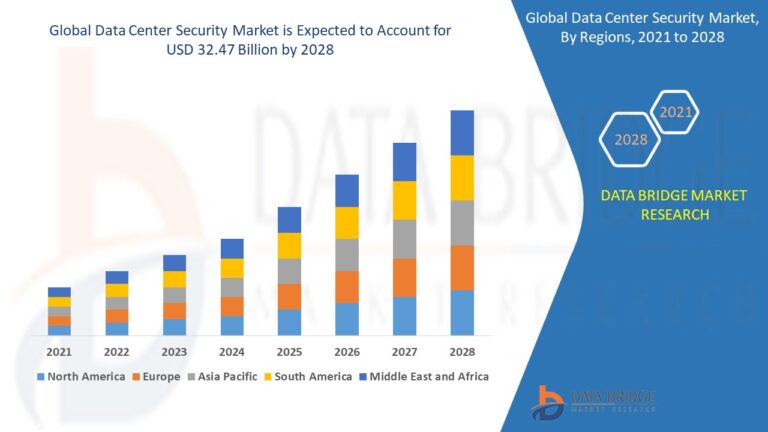
Growth Rate of Data Center Security Market
The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the data center security business is predicted to be 16.84% between 2021 and 2028, according to data bridge market research. Data center security is expected to be a USD 32.47 billion market by 2028, according to this estimate.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-data-center-security-market
Conclusion
Protecting sensitive information in data centers is a complex and ongoing challenge that requires a multi-layered approach to security. By implementing best practices in physical security, network security, data security, and cybersecurity, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and ensure the integrity and availability of their critical assets. Additionally, staying compliant with regulatory requirements and investing in employee training and awareness can further strengthen the organization’s data center security posture. As cyber threats continue to evolve, organizations must remain vigilant and adapt their security strategies to address new challenges, ensuring the continued protection of sensitive information in the digital age.