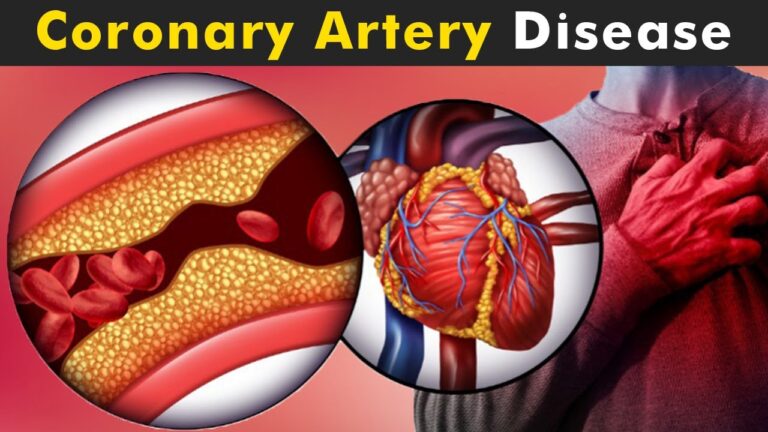
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is one of the most common heart conditions, affecting millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. This can lead to chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, and, in severe cases, heart attacks. Understanding Coronary Artery Disease treatment and management is essential for improving heart health and preventing complications. Let’s take a closer look and learn more.
What Causes Coronary Artery Disease?
CAD is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, a condition where fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances accumulate on the inner walls of the coronary arteries. This buildup, known as plaque, can harden and narrow the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle. Several risk factors contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and CAD, including:
- High cholesterol levels
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Unhealthy diet
- Family history of heart disease
- Age and gender (men over 45 and women over 55 are at higher risk)
These factors can damage the coronary arteries over time, leading to the gradual development of CAD.
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
The symptoms of CAD can vary depending on the severity of the disease. Some people may not experience any symptoms until the disease has progressed significantly. Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina): This is the most common symptom, often described as a pressure or squeezing sensation in the chest. It may also radiate to the shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back.
- Shortness of breath: Reduced blood flow to the heart can cause difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity.
- Fatigue: People with CAD may feel unusually tired, even with minimal exertion.
- Heart attack: In severe cases, a complete blockage of the coronary artery can lead to a heart attack, which requires immediate medical attention.
Diagnosing Coronary Artery Disease
Diagnosing CAD involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Some of the most commonly used tests include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test measures the heart’s electrical activity and can detect abnormal rhythms or areas of damage.
- Stress test: During a stress test, the heart’s activity is monitored while the patient exercises on a treadmill or stationary bike. This helps determine how well the heart functions under physical stress.
- Echocardiogram: This ultrasound test provides images of the heart’s structure and function, allowing doctors to assess the movement of the heart walls and the efficiency of the heart valves.
- Coronary angiography: This is an invasive procedure where a contrast dye is injected into the coronary arteries through a catheter. X-ray images are then taken to visualise any blockages or narrowing in the arteries.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can check for elevated cholesterol levels, blood sugar, and markers of inflammation, which are associated with an increased risk of CAD.
Coronary Artery Disease Treatment
Coronary Artery Disease treatment aims to relieve symptoms, reduce the risk of heart attacks, and prevent further progression of the disease. Treatment plans are tailored to each patient’s specific condition, taking into account the severity of the disease, overall health, and lifestyle. The main treatment options include lifestyle changes, medications, and surgical procedures.
1. Lifestyle Changes:
Lifestyle modifications are the cornerstone of CAD management and can significantly improve heart health. These changes include:
- Healthy diet: A heart-healthy diet reduces saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol. It includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats (such as those found in nuts, seeds, and fish).
- Regular exercise: Physical activity helps improve cardiovascular fitness, lower blood pressure, and maintain a healthy weight. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps to reduce the risk of CAD. Smoking damages the blood vessels and accelerates the buildup of plaque.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help reduce the strain on the heart and lower the risk of CAD.
- Stress management: Chronic stress can negatively affect heart health. Meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels.
2. Medications:
Medications are often prescribed to manage symptoms, lower risk factors, and prevent complications in CAD patients. Commonly used medications include:
- Anti-platelet agents: These drugs, such as aspirin, help prevent blood clots from forming in the arteries.
- Statins: Statins are prescribed to lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Beta-blockers: These medications reduce the heart rate and blood pressure, decreasing the heart’s workload.
- ACE inhibitors: Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors help relax blood vessels, lower blood pressure, and reduce the strain on the heart.
- Calcium channel blockers: These drugs help relax and widen blood vessels, improving blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Nitroglycerin: Nitroglycerin is used to relieve chest pain (angina), and it helps dilate the coronary arteries, improving blood flow.
3. Surgical Procedures:
In cases where lifestyle changes and medications are not sufficient, surgical procedures may be necessary to restore blood flow to the heart. The most common procedures include:
- Angioplasty and stenting: Angioplasty involves inserting a balloon-tipped catheter into the narrowed artery and inflating it to widen the artery. A stent (a small mesh tube) is often placed in the artery to keep it open.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG): CABG is a surgical procedure where a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body is grafted onto the blocked coronary artery, creating a new pathway for blood to flow to the heart muscle.
- Atherectomy: This procedure involves using a catheter with a rotating blade or laser to remove plaque from the artery walls.
Conclusion
Coronary Artery Disease is a serious condition that requires careful management and treatment to prevent complications and improve quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for CAD, patients can take proactive steps to protect their heart health.
Choosing the right hospital for CAD treatment is crucial, and hospitals like Nanavati Max Super Specialty Hospital in Mumbai stands out as an excellent choice for comprehensive cardiac care. With its advanced medical facilities, experienced medical team, and patient-centred approach, Nanavati Max Hospital offers the highest standard of care for patients with CAD. By focusing on treatment and prevention, the hospital ensures patients receive the best possible care to manage their condition and lead healthier lives.